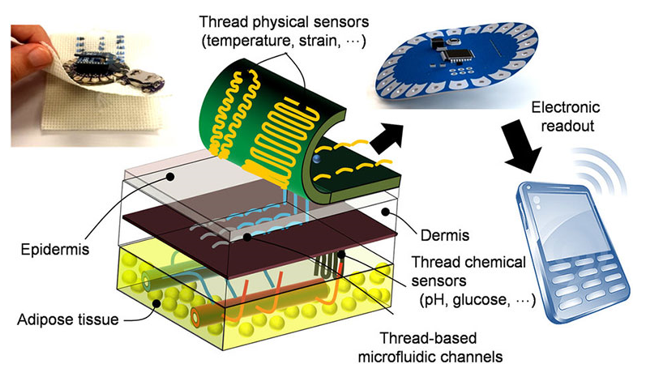
Novel 3-D “Smart” Sutures for Wireless Collection of Biological Data
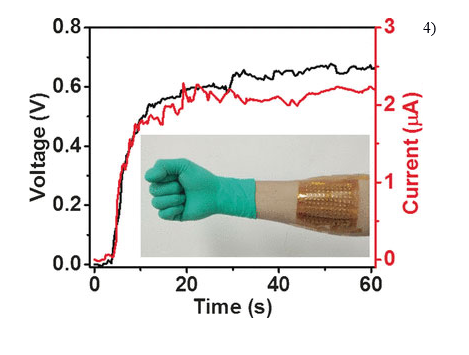
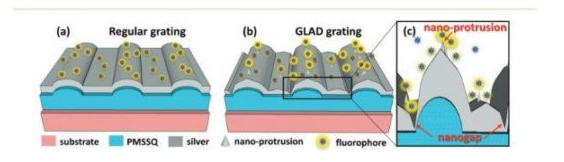
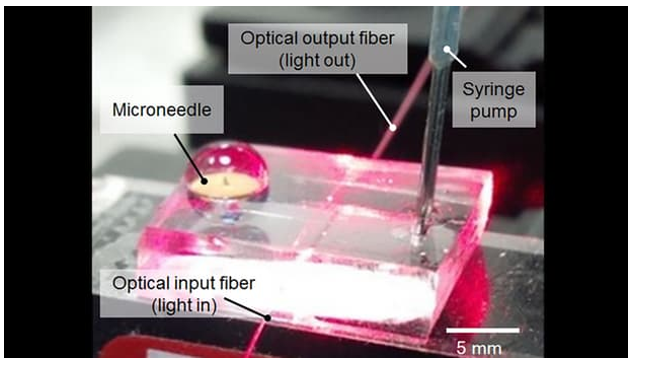
The field of smart wearable systems has just gotten a boost thanks to researchers from Tufts University. A team of engineers has developed a novel 3-dimensional thread-based diagnostic platform that, when sutured into tissue, collects a range of real-time diagnostic data wirelessly, including pH, glucose levels, temperature, stress, strain, and pressure. Physical and chemical nanosensors, microfluidics, and electronics integrated into various types of conductive threads, including cotton and synthetic fibers, are connected to a wireless electronic circuit. The result is a suture that can penetrate tissue, sense various factors in…
Read More